X-Ray Technicians and Radiation Therapists: A Comparative Overview
Introduction
In the medical field, X-ray technicians and radiation therapists are two essential professionals who contribute significantly to patient care and treatment. While their roles may seem related due to their use of imaging and radiation, they perform distinct functions and require different training. This article explores the key aspects of each profession, highlighting their responsibilities, training requirements, and the differences between them.
What is an X-Ray Technician?
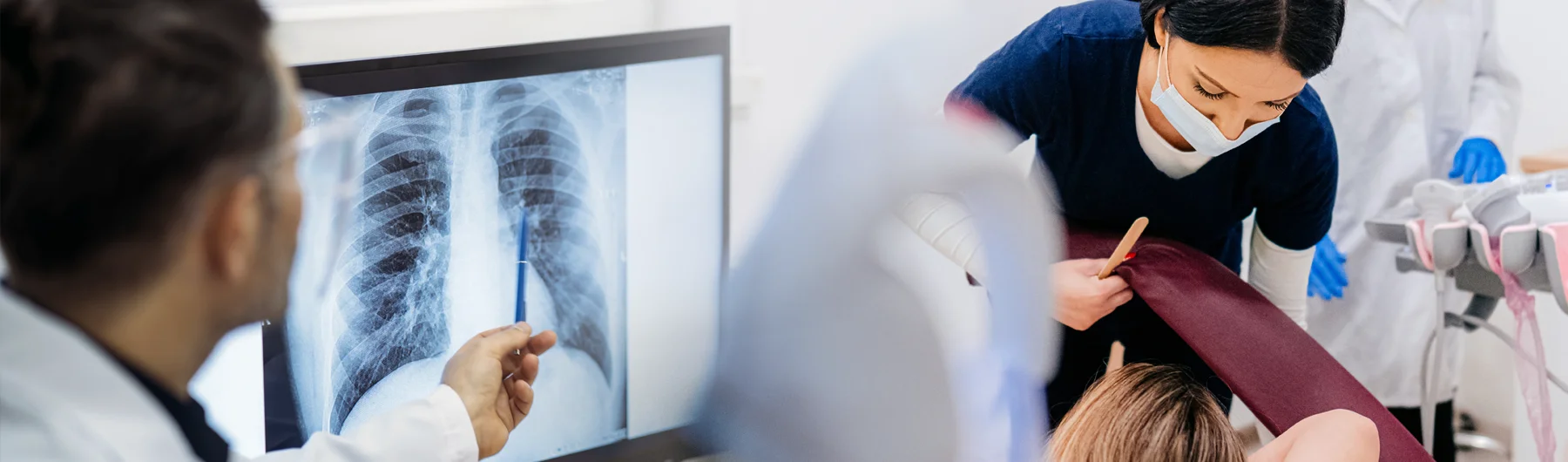
An X-ray technician, also known as a radiologic technologist, is a healthcare professional specialized in using imaging equipment to capture detailed images of the body’s internal structures. These images, called radiographs, are crucial for diagnosing a wide range of medical conditions, including fractures, infections, and tumors.
X-ray technicians are responsible for positioning patients correctly and operating the imaging equipment to obtain clear and accurate images. They ensure that patients are comfortable and understand the procedure, which often involves explaining how to hold still or hold their breath during the imaging process. Technicians also maintain and calibrate their equipment to ensure it functions properly and safely.
Although X-ray technicians do not interpret the images themselves, they play a crucial role in ensuring that the images produced are of high diagnostic quality, which radiologists then review.
Education and Training for X-Ray Technicians
To become an X-ray technician, individuals typically need to complete an accredited radiologic technology program. This program can lead to either an associate’s degree or a bachelor’s degree and includes coursework in subjects like anatomy, patient care, and radiologic physics. Additionally, students gain practical experience through clinical rotations. Certification from a recognized body, such as the American Registry of Radiologic Technologists (ARRT), is often required to practice professionally.
What is a Radiation Therapist?
A radiation therapist is a specialized healthcare professional who administers radiation treatments to patients with cancer or other conditions requiring radiation therapy. They work closely with oncologists to deliver precise doses of radiation to targeted areas of the body, aiming to destroy cancer cells while minimizing damage to surrounding healthy tissue.
Radiation therapists prepare and administer radiation treatments based on detailed treatment plans provided by oncologists. They interact with patients to explain the treatment process, address any concerns, and monitor patients for potential side effects during the course of their therapy. The role also involves operating advanced equipment, such as linear accelerators, to ensure accurate and effective delivery of radiation.
Education and Training for Radiation Therapists
To become a radiation therapist, individuals usually complete a specialized radiation therapy program that leads to an associate’s degree or a bachelor’s degree. This education covers a range of topics including radiation physics, oncology, and patient care, along with clinical training. Certification from the American Registry of Radiologic Technologists (ARRT) or a similar organization is generally required for professional practice.
Key Differences Between X-Ray Technicians and Radiation Therapists
The primary difference between X-ray technicians and radiation therapists lies in their focus and responsibilities. X-ray technicians concentrate on diagnostic imaging to aid in the diagnosis of medical conditions. They operate X-ray machines and other diagnostic equipment to capture images that help identify issues such as fractures, infections, or tumors.
In contrast, radiation therapists are focused on delivering therapeutic radiation treatments to patients, primarily those with cancer. They operate sophisticated radiation therapy equipment and are involved in the ongoing care of patients undergoing radiation therapy, monitoring their progress and managing any side effects.
Career Outlook and Opportunities
Both X-ray technicians and radiation therapists have promising career prospects, with opportunities for specialization and advancement in their respective fields. X-ray technicians may choose to specialize in areas such as computed tomography (CT) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), while radiation therapists might advance to roles in treatment planning or management. The demand for both professions is expected to grow, driven by technological advancements and an aging population.
Conclusion
X-ray technicians and radiation therapists are both integral to modern healthcare, but they serve different roles within the medical field. X-ray technicians focus on diagnostic imaging to aid in identifying medical conditions, while radiation therapists specialize in delivering targeted radiation treatments for cancer and other conditions. Understanding these roles and their specific requirements can help individuals make informed decisions about their career paths in healthcare.

